ALAC vs FLAC: Which Lossless Format Is Best for Your Library?


If you’re curating a high-quality music collection, you’ve probably come across the battle of ALAC vs FLAC at some point. These two popular lossless audio formats preserve every detail of the original recording, allowing for a richer, fuller listening experience than compressed files like MP3. While Apple users tend to gravitate towards ALAC, FLAC is widely supported on most platforms. In this article, we’ll explain the differences between ALAC and FLAC, so you can make the best choice for your music library.
Understanding ALAC vs FLAC
If you’ve ever wondered, “Is Apple Lossless as good as FLAC?”, the short answer is yes, in terms of audio quality. ALAC and FLAC are both lossless audio formats, which means they’re identical to the source recording. They both preserve the full quality of the audio while compressing the file to take up less space than an uncompressed format like WAV or AIFF. The differences come in compression efficiency, compatibility, and which devices you’re using them with.
What is ALAC?

ALAC stands for Apple Lossless Audio Codec, and it’s exactly what it sounds like: lossless audio compression developed by Apple. ALAC achieves bit-for-bit accuracy of the original recording while compressing the file down to a smaller size than WAV or AIFF. It’s fully supported across Apple software and devices, which makes it the native format for iTunes, macOS, and iOS devices. ALAC was originally a proprietary codec but was released as open source in 2011 by Apple. After that, it’s primarily been used among Apple users.
What is FLAC?

FLAC is an open-source, Free lossless audio codec that’s supported by many different platforms and devices. It offers full lossless quality identical to the source recording, but generally with better compression than ALAC. FLAC files have smaller file sizes on average while maintaining the same sound quality. FLAC has become one of the most popular lossless audio formats among audiophiles because it’s versatile, compatible, and offers great metadata support, but it’s not supported natively on Apple’s Music app.
ALAC vs FLAC: Comparison Table
| Feature | ALAC | FLAC |
|---|---|---|
| File Extension | m4a | flac |
| Audio Quality | Lossless, same as source | Lossless, same as source |
| Compression | Slightly larger file size | More efficient compression |
| Compatibility | Best with Apple devices/software | Works on most OS and devices |
| Metadata Support | Full metadata support | Full metadata support |
| File Size | Slightly bigger than FLAC | Slightly smaller than ALAC |
ALAC vs FLAC: Detailed Comparison
In terms of ALAC vs FLAC, the real differences don’t lie only in sound quality; they lie in compression efficiency, file size, and device compatibility. Let’s take a deeper look at the three factors and figure out which format is best for your music library.
1. ALAC vs FLAC Sound Quality
In terms of performance, there’s no practical difference between the audio quality of ALAC and FLAC. Both offer true lossless compression, which means the file is identical to the original source material. There’s no quality loss, no distortion, and no missing detail with either format. The only thing to keep in mind is that both ALAC and FLAC will always be best with high-resolution lossless audio files (Hi-Res FLAC or ALAC files) rather than MP3 or AAC. In other words, the format doesn’t change the audio quality; only the quality of the file itself will matter.
2. Compression Efficiency
Compression efficiency is where FLAC generally takes the lead against ALAC. FLAC has better compression ratios on average, which results in smaller file sizes while maintaining identical quality to ALAC. This can be a great benefit if you’re limited on storage space or want faster file transfers over low-speed connections. It’s also the main reason some people choose FLAC over ALAC for no reason other than smaller file sizes. That said, the size difference between ALAC and FLAC is usually marginal and is typically not a make-or-break issue.
3. Compatibility and Device Support
Device compatibility is where the most substantial distinction between the two lies. ALAC has deep integration with Apple’s entire ecosystem, which means it works seamlessly with iTunes, Apple Music, iOS devices, and macOS. FLAC, on the other hand, has much more widespread support on different operating systems, including Windows, Linux, Android, and standalone audio players.
ALAC vs FLAC: Which One Should You Choose?
Since the sound quality of ALAC and FLAC is practically identical, the choice between the two comes down to the devices you own and which ecosystem you use. If you’re deeply entrenched in Apple devices like the iPhone, iPad, Mac, or Apple Music, ALAC is the clear choice because it integrates natively and works seamlessly. On the other hand, if you want the widest possible support across all platforms and devices, FLAC is the better option. FLAC works right out of the box on Windows, Linux, Android, and many standalone music players. It’s also the ideal choice if you want your files to be playable anywhere without converting. FLAC also has a slight edge in terms of compression, resulting in slightly smaller files.
How to Convert Between ALAC to FLAC with Lossless Quality?
If you have a music library containing both ALAC and FLAC files, you might want to convert them for better compatibility without losing quality. Whether you’re switching from Apple devices to other platforms or vice versa, a reliable lossless converter ensures your music stays exactly as it should sound. OneConv Audio Converter is a versatile media converter that handles both audio and video formats with ease, delivering high-speed, 100% lossless conversions. With its simple interface, wide format support, and efficient batch processing, it’s an excellent choice for converting ALAC to FLAC or the other way around without sacrificing sound quality.
- 100% Lossless Audio Conversion: Keeps the exact sound quality of your original files.
- Ultra-Fast Speed: Converts large audio libraries up to 10x faster than standard tools.
- Multiple Format Support: Works with FLAC, ALAC, MP3, AAC, WAV, OGG, and more.
- Batch Conversion: Process entire music collections in one go for time efficiency.
Step 1 Download and install OneConv on your computer.
Step 2 Launch OneConv and choose FLAC as the output format in the Convert section.
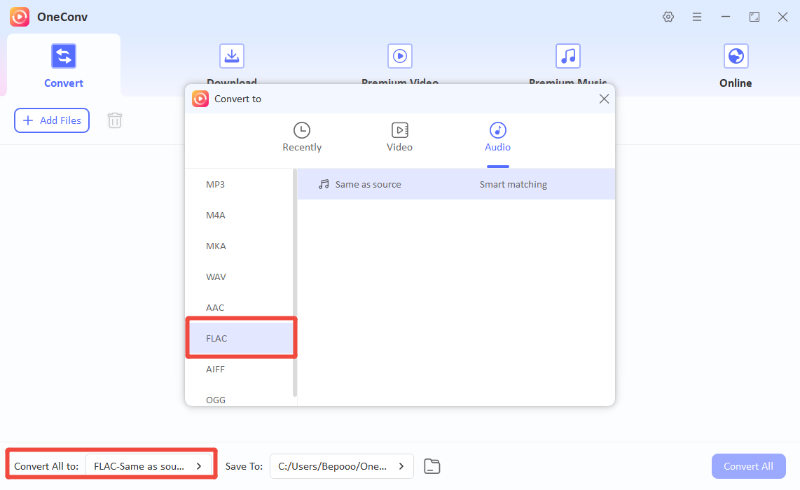
Step 3 Open OneConv and click “Add Files” to import the ALAC music files you want to convert.
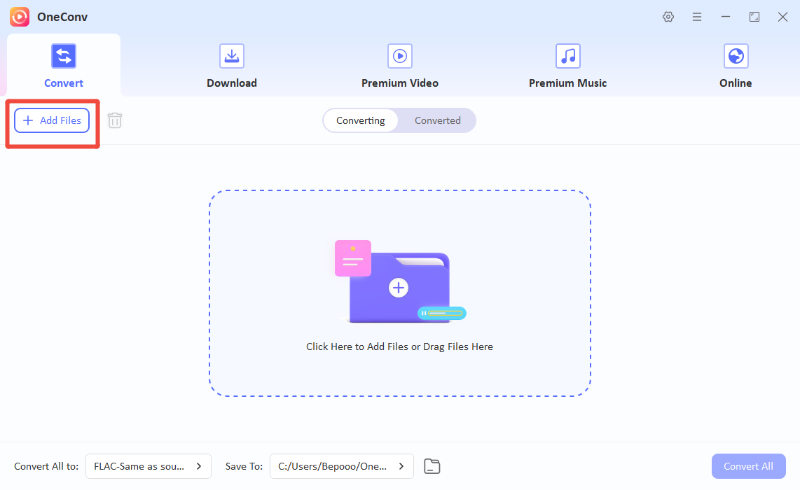
Step 4 Click “Convert All” to start the conversion. Your favorite tracks will be converted to the desired format in seconds.
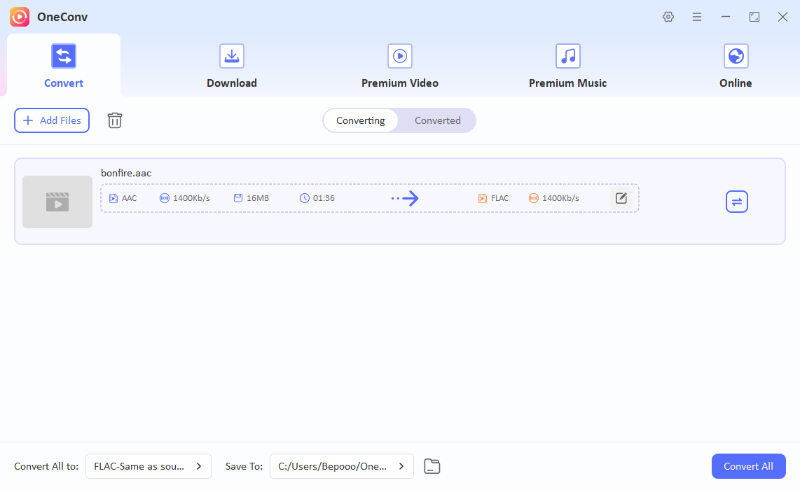
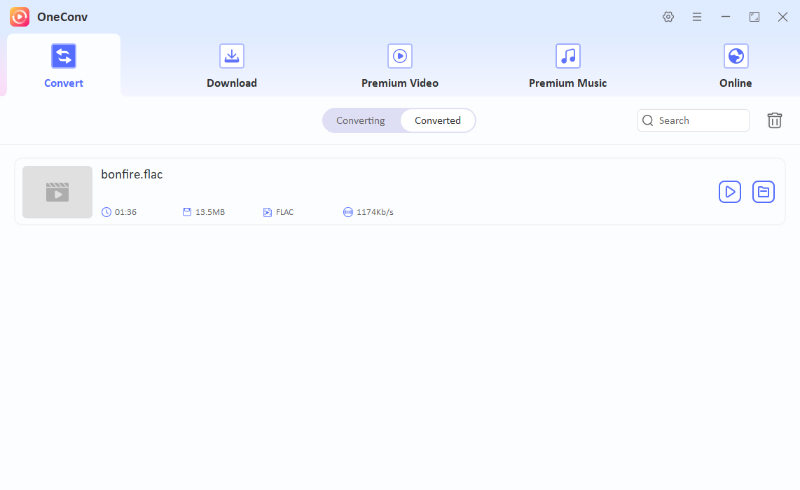
Step 5 After the conversion completes, you can check all converted files in the Converted folder.
FAQs about ALAC vs FLAC
- Q. Will I lose quality converting between ALAC and FLAC?
- No. Both are lossless formats, so converting between them with the right tool will preserve the exact original quality.
- Q. Are ALAC and FLAC both actual lossless?
- Yes. ALAC (Apple Lossless Audio Codec) and FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec) both store audio without any loss of quality.
- Q. Can I play FLAC files on my iPhone or iPad?
- Not directly with Apple’s native Music app, but you can use third-party apps or convert FLAC to ALAC for full compatibility.
Final Words
When it comes down to the differences of ALAC vs FLAC, the choice mostly comes down to your devices and the ecosystem you use, rather than which has better sound quality. ALAC is deeply integrated into Apple’s whole system, while FLAC offers broader cross-platform support and slightly better compression. If you need to switch between the two formats, OneConv makes the conversion process quick, simple, and completely lossless. With a few clicks, you can convert your file to any of your preferred formats.